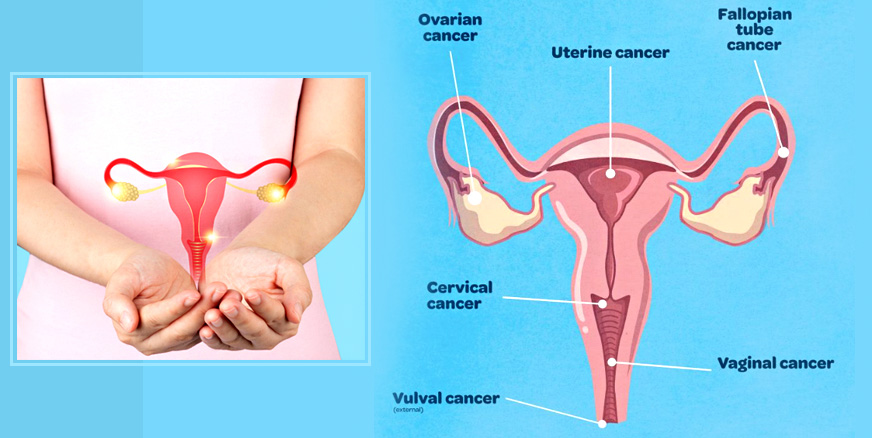
Gynecologic cancer is any cancer that starts in a woman’s reproductive organs. Cancer is always named for the part of the body where it starts. Gynecologic cancers begin in different places within a woman’s pelvis, which is the area below the stomach and in between the hip bones.
Types of Gynecologic Cancer
Cervical cancer
begins in the cervix, which is the lower, narrow end of the uterus. (The uterus is also called the womb.)
Ovarian cancer
begins in the ovaries, which are located on each side of the uterus. Some ovarian cancers can also begin in the fallopian tubes or peritoneum.
Uterine cancer
begins in the uterus, the pear-shaped organ in a woman’s pelvis where the baby grows when she is pregnant.
Vaginal cancer
begins in the vagina, which is the hollow, tube-like channel between the bottom of the uterus and the outside of the body.
Vulvar cancer
begins in the vulva, the outer part of the female genital organs.
Each gynecologic cancer is unique, with different signs and symptoms, different risk factors (things that may increase your chance of getting a disease), and different prevention strategies. All women are at risk for gynecologic cancers, and risk increases with age. When gynecologic cancers are found early, treatment is most effective.
Common Symptoms of Gynecologic Cancers
Common Symptoms with as below,
- Abnormal Bleeding from the vagina especially in post menopausal women or intermenstrual bleeding or bleeding after intercourse.
- Abdominal bloating or swelling with or without backpain in Ovarian Cancers
- Lower abdominal pain or discomfort
- Itching or burning or tenderness of the vulva and changes in colour of the vulva or rash or sores or warts.
How Are Gynecologic Cancers Treated?
Gynecologic cancers are treated in several ways. It depends on the kind of cancer and how far it has spread. Treatments may include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation. Women with a gynecologic cancer often get more than one kind of treatment.
- Surgery: Doctors remove cancer tissue in an operation.
- Chemotherapy: Using special medicines to shrink or kill the cancer. The drugs can be pills you take or medicines given in your veins, or sometimes both.
- Radiation: Using high-energy rays (similar to X-rays) to kill the cancer.
If your doctor says that you have a gynecologic cancer, ask to be referred to a gynecologic oncologist—a doctor who has been trained to treat cancers of a woman’s reproductive system. This doctor will work with you to create a treatment plan.
Surgeries Performed successfully
- Radical Hysterectomy for Cervix and Ovarian Cancers